The intersection of customer experience (CX) and employee experience (EX) has become an undeniable focus of technology innovation. Initially, the spotlight was primarily on CX, with technologies being honed to streamline, enhance, and personalize the customer journey. This investment was driven by an understanding that a positive CX was a critical driver of business success, with its impact measurable through direct correlations with customer loyalty, retention, and advocacy.
A pivot occurred when tangible data began to illuminate a direct linkage between CX and EX. IDC studies have shown that the engagement level of employees is intrinsically tied to the quality of customer service they deliver. And the good news is, as leaders became more aware of this connection, there was a marked shift in strategic priorities. Companies started to invest in technologies that improved not just the customer journey but also the employee’s day-to-day workflow. The rationale was clear: by enabling employees with better tools and processes, they could perform their roles more effectively and efficiently, leading to a direct uplift in customer satisfaction.
Business shared services have a long-standing application to support employees internally, yet, transformation in these services has not been at the forefront of digital transformation. Shared services strive for organizational efficiency, cost reduction, and process unification by capitalizing on large-scale operations and niche expertise. This model consolidates fundamental supportive functions—like HR and finance—into a unified resource for various company divisions. Employees in these contexts are indeed the internal customers that require the services from these shared functions.
Nonetheless, shared service execution currently encounters obstacles, such as inaccuracies and delays, which disrupt operations, hinder adaptability, and can lead to decreased customer satisfaction. A recent IDC report highlights that employees across all industries prefer to have their service requests completed in half of the time as they are currently.
In the world of shared services where automation meets satisfaction
In the Asia-Pacific region, shared services have become a cornerstone for organizational support, particularly in IT, finance, legal, HR, and procurement (see figure below). These shared services are heavily process-oriented, streamlining repetitive and routine tasks across these critical functions. Their process-driven nature renders them ideal for the integration of automation and artificial intelligence. As these sectors typically involve repetitive and rule-based tasks, they stand to gain significantly from the efficiency, accuracy, and scalability that AI and automation technologies can provide, transforming the landscape of shared services with innovation and smart systems. As AI and automation are among the top technology investments for Asia/Pacific businesses in 20241 , IDC anticipates that these technologies will be more widely applied to improve shared services.
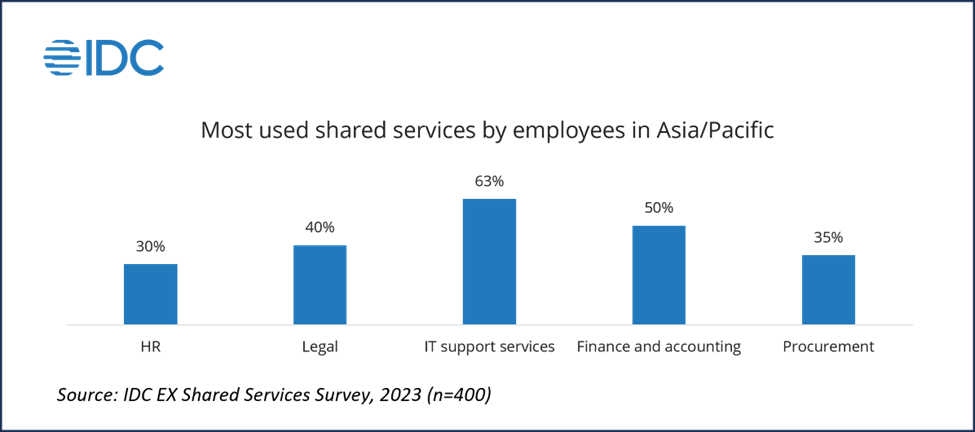
There are many potential use cases that automation and GenAI can be applied to improve the most used shared services for employees in Asia/Pacific. For example, intelligent automation can significantly enhance IT shared services by streamlining ticketing processes, where machine learning algorithms predict and categorize ticket issues, enabling faster resolution times. Automation of routine tasks, such as password resets and system updates, frees up IT staff for more complex problem-solving. Additionally, AI-driven analytics can proactively monitor systems for patterns that could indicate potential issues, allowing for preemptive maintenance and minimizing downtime. This tech-forward approach not only improves operational efficiency but also elevates the user experience for employees relying on these crucial IT services.
In HR, GenAI can improve individual self-service by automatically recommending workflows across HR and non-HR applications, directing employees by query to the tools, resources, and insights they need. This way, employees can find HR-related queries with tailored information, reducing the reliance on HR support, and in shorter processing time.
For legal requests, automation and GenAI can greatly enhance the efficiency of legal shared services by automating the drafting and review of standard legal documents, which reduces the time legal teams spend on routine work. AI can assist in analyzing contracts to ensure compliance with laws and corporate policies, and machine learning models can predict legal risks by comparing against historical data, which is usually a time-consuming process. This allows attorneys to focus on more strategic tasks that require their expertise and judgment, thus improving the overall responsiveness and effectiveness of legal shared services.
In procurement, automation and GenAI can streamline the requisition-to-purchase process. For instance, GenAI can predict purchasing needs based on historical data, automate the creation of purchase orders, and assist in vendor selection by analyzing vendors’ past performance and compliance. Moreover, AI can negotiate prices within predefined parameters, carry out transactional procurement tasks, and manage inventory in real-time, significantly improving efficiency and reducing manual errors in procurement operations.
In the realm of finance shared services, automation and GenAI can be pivotal in transforming tasks such as expense management and report generation. For instance, AI can automatically categorize expenses based on learned behavior, while also flagging anomalies for review. Similarly, AI can generate predictive financial reports, offering insights based on data trends, and facilitate faster month-end closures by automating data entry and reconciliation tasks. This not only streamlines finance operations but also provides more accurate, real-time financial data to inform strategic decision-making.
IDC has recently published several Taxonomy use cases documents on the potential application of GenAI in enhancing the 13 functional areas including IT, HR, procurement, legal and finance mentioned in this article.
Automation doesn’t make us bots, it’s giving employees more time to be human
Our IDC EX Shared Services Survey, 2023 data shows that 66% of the employees believe that automating shared services within organizations can significantly improve employee satisfaction, which is rated the number one benefit of shared service optimization. It also enhances process accuracy, with a 55% improvement, ensuring that tasks are completed correctly the first time. Additionally, a 46% time savings shows that automating shared services allows organizations to operate more efficiently, freeing up staff to focus on more strategic activities. These benefits collectively contribute to a more productive and contented workforce.
Moreover, automating shared services can drastically reduce task completion times, freeing up employees to focus more on innovation, with 60% of their time being redirected towards creative and strategic initiatives. With less time spent on process-oriented tasks, employees can spend 50% more time on core organizational activities like Diversity & Inclusion, or ESG. Automation also allows a 43% increase in efforts dedicated to refining processes, leading to continuous operational enhancements and value creation within the organization.
While the data showcasing the advantages of process automation in shared services is encouraging, it’s crucial for leaders to recognize the necessity of investing in these systems. Automation of processes, including those in shared services, is pivotal in enhancing both the employee experience (EX) and customer experience (CX). Committing resources to enhance workflows and employee satisfaction should be viewed not as a mere expense but as a strategic investment that yields long-term benefits.
For more on unlocking the power of automation to optimize business-shared services, please check out this IDC Survey.
1 IDC Survey 2023: AP DX Executive Sentiment Survey, n=810




