In the digital business era, transformative advancements have reached unprecedented heights, driving rapid digital transformation and widespread cloud adoption across industries. This transformation has profoundly impacted customer experiences, enabling companies to offer seamless, personalized, real-time interactions across multiple touchpoints. By leveraging digital technologies and cloud capabilities, enterprises can create meaningful and engaging experiences that set them apart in the competitive digital economy.
However, this shift to cloud-based solutions has also led to an expansion of attack surfaces, creating newer areas of vulnerability. From smartphones and tablets to IoT devices and wearables, the proliferation of interconnected devices has resulted in a complex and vast digital landscape, each representing a potential entry point for cyberattacks.
Cyberthreat Landscape in Asia/Pacific
Cyberattacks worldwide are escalating at an alarming rate, becoming highly targeted and sophisticated. Cybercriminals continuously develop more intelligent methods to exploit vulnerabilities, steal sensitive data, or demand ransom. Securing all connected applications to critical infrastructure becomes more challenging, making it easier for attackers to find vulnerabilities to exploit, including the use of bots for both legitimate and malicious purposes. As a result, businesses face frequent, targeted, and complex cyberattacks, leading to significant financial burdens, customer attrition, and damage to brand reputation.
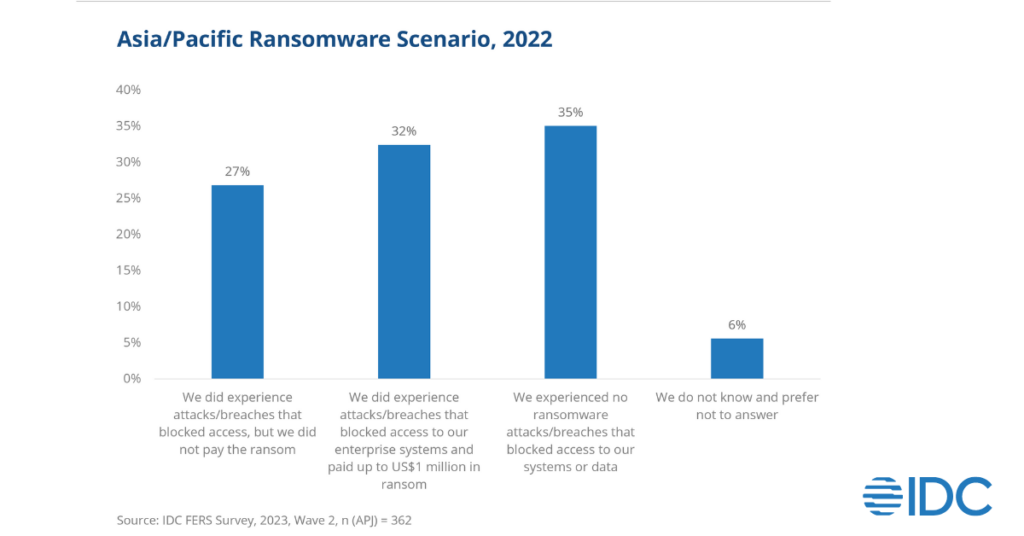
The Asia-Pacific Japan (APJ) region has seen a surge in cyberattacks, with a cyberthreat landscape that is intricate and constantly evolving. The region is influenced by geopolitical tensions, rapid digitalization, and the growing expertise of cybercriminals and state-sponsored hackers. According to IDC’s 2023 Future Enterprise Resiliency and Spending (FERS) Survey, Wave 2, a staggering 59% of enterprises in APJ fell victim to ransomware attacks in 2022, and 32% ultimately paid the ransom. Out of these, Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, and India were the worst affected regions. Among the affected businesses, 97% reported that the impact lasted from a single day to several weeks. This signals that now is the opportune moment for enterprises to strategically invest in cutting-edge technologies for proactive threat detection and decisive attack mitigation.
Significant Advancements in Threat Detection and Response
Today’s cyberthreat landscape has led to the emergence of EDR (End Point Detection and Response) and XDR (Extended Detection and Response) solutions backed by MDR (Managed Detection and Response)services to detect and respond to cyber threats. Early detection allows organizations to prevent or limit the damage caused by attacks, reducing data loss and minimizing the attack’s impact. According to IDC’s 2023 FERS Survey, Wave 2, 71.5% of the surveyed enterprises in APJ mentioned that threat detection and response tools, including EDR, NDR and SIEM (Security information and event management), helped them detect attacks before intruders had a chance to act.
EDR has become essential in enterprise cybersecurity strategies, used by organizations of all sizes and industries to protect their endpoints from cyberthreats. MDR services offer a comprehensive approach to shield businesses from advanced and frequent cyberthreats, delivered by experienced cybersecurity experts in a 24 x 7 remote SOC with cutting-edge solutions and hands-on support. As per IDC’s Asia/Pacific IT Services Survey, 2022, majority of the enterprises stated that the most important capabilities they seek in an MDR provider, is the ability to effectively integrate network and endpoint at the architectural level for enhanced visibility into assets and proactive threat detection at all surfaces. Apart from this, they also require an MDR provider to offer strong analytical capabilities. Some enterprises also indicate the need for a third-party analytical platform that can help absorb inputs from web, email, network, endpoints as well as cloud and deliver a comprehensive threat analysis. This is exacerbated by the need to have a proactive threat hunting for knowns and unknowns including third-party risk assessments from all sources as well as a well-suited and integrable range of threat detection and response offerings.
Enterprises are now directing their investments towards XDR solutions, empowering them to identify and effectively counter threats across networks, endpoints, and cloud environments. With advanced analytics, XDR solutions can form complex correlations between relevant data sources, reducing false positives and improving threat detection. IDC emphasizes that every XDR solution should include EDR capabilities, which can be enhanced with NDR, (Network Detection and Response) integration with external threat intelligence, and an underlying log management backplane, providing alerts from virtualized resources over the cloud.
The XDR solutions must also incorporate a SOAR solution for workflow management, DDoS Security, a WAF, web and email defense, identity and access management (IAM), data loss prevention (DLP), workload management, and FIM. XDR platforms are known for their scalability, reliability, extensibility, and modularity. While many XDR tools are cloud-based, some organizations prefer dedicated or on-premises solutions or a hybrid approach due to concerns about public cloud environments. Regardless of the chosen approach, a cloud-based XDR solution offers accessibility and flexibility for experts and analysts working in hybrid setups. A comprehensive XDR solution much in demand these days helps assist enterprises with threat quarantine, automated and manual remediation, alert escalation, reporting, and forensic analysis and must be the focus area for security service providers looking to cater to future enterprises.
Proactive detection and response may only sometimes be sufficient, particularly as cybercriminals adopt multi-vector approaches. The threat landscape’s complexity has led to the evolution of threat detection, including signature-based and behavior-based detection, threat intelligence, automation and orchestration, integration with incident response, and deception technology.
Using AI for TI – Threat Intelligence
AI-powered threat hunting leverages ML and data analytics to uncover hidden patterns and anomalies, improving the identification of potential threats. Businesses are now investing in threat hunting solutions that deploy AI/ML capabilities to predict threats based on historic patterns, addressing known and unknown threats with relevant insights and minimal false positives using comprehensive security analytics. AI’s relationship with threat detection and response is symbiotic, enabling more accurate and efficient threat detection, facilitating faster incident response and remediation, and empowering security analysts with advanced tools to proactively hunt for threats.
The potential use cases for threat intelligence are a significant leap forward compared to detection and response strategies. A prime example is identifying adversaries, a captivating aspect of threat intelligence, as it traces known threat vectors back to the responsible miscreant be it a cybergang or a nation-state sponsored attacker. Moreover, threat intelligence platforms can collect and correlate data from in-house security tools, including SIEM, UEBA, IDS/IPS, and antivirus software. This grants insights, validates possible insider threats, and supports external intelligence for forensic investigations.
The ever-evolving threat intelligence feeds necessitate consistent cross-referencing with up-to-date IoCs, such as behaviors, tactics, exploits, and open source code vulnerabilities. Here, automation plays a pivotal role in artifact collection, thereby ensuring accuracy. Additionally, there are times when unmanaged devices within a network can become inadvertent targets for attackers due to misconfigurations, incomplete patch management, or other issues. Threat intelligence also mitigates the challenges of shadow IT or enhances detection across data graveyards.
Remarkably, specific threat intelligence solutions cater to industrial control systems, APT intelligence, crime, and forensics intelligence. In the transportation industry, enterprises are leveraging threat intelligence to proactively prepare for attacks and fortify their infrastructure. Notably, a major Indian insurance company utilized threat intelligence to thwart 3.4 billion INR worth of fraud across various domains, integrating AI technology to enhance the fraud investigation process.
In the current landscape, establishing strategic partnerships between threat intelligence vendors and service providers holds the utmost significance. Enterprises seeking relief from financial and operational burdens desire consolidated service offerings. This market shift calls for security service providers to offer comprehensive solutions, including SOC, vulnerability assessments, incident management, and threat intelligence. Cultivating strong and strategic partnerships is pivotal for ensuring a unified, all-encompassing approach that aligns with evolving customer demands. Additionally, collaborative partnerships between security vendors and service providers aimed at delivering advanced threat intelligence capabilities and solutions by seamlessly blending global threat data with localized insights will offer a robust framework and a comprehensive perspective to potential clients on threats that hold significance in their unique operational context. This synchronized approach empowers organizations to stay ahead of evolving cyber risks and enhance their security posture.
Advice for Enterprises
For enterprises looking to adopt or elevate their threat detection and response capabilities, initiating efforts to reduce dwell time typically involves starting with EDR. However, sophisticated attacks often encompass more than just endpoints, necessitating the adoption of XDR as the next evolutionary step. Technology buyers are advised to assess their requirements and then look at investing in a multitude of advancements happening with the advent of AI/ML models in the threat hunting and threat intelligence space as an advancement to detection and response.
When selecting threat intelligence vendors, technology buyers should remember to prioritize those offering contextual insights that align with their industry and environment. It’s crucial to assess vendors based on their ability to provide actionable insights, enabling proactive defense strategies and swift responses to emerging threats. Integration capabilities are key, ensuring seamless collaboration with existing security tools and infrastructure. Look for vendors who blend global and local threat data to offer a comprehensive perspective and consider their automation and data enrichment capabilities to enhance threat detection accuracy. Scalability is essential to accommodate growth and evolving threat landscapes. Additionally, evaluate vendors using real-performance metrics such as Mean Time To Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time To Respond (MTTR) to ensure their effectiveness in rapid threat identification and resolution.
This approach ensures that your chosen threat intelligence vendor aligns with your organization’s unique needs and contributes to a robust security posture. Also, it is always essential to note that AI is not a silver bullet and should be used with human expertise, as security analysts play a critical role in validating and interpreting AI findings within the organization’s environment to make informed decisions regarding threat response and mitigation. Without a doubt, the collaboration between AI and human intelligence undoubtedly bolsters an organization’s overall security posture.
Get insight on adoption and perception of threat intelligence solutions by Indian enterprises in this on-demand IDC webinar here.
Interested in how enterprises should strategize their investments moving forward?




