Content consumption of video and video-like data has changed dramatically over recent years with online streaming and gaming is a new norm. The COVID pandemic has dramatically altered the mode of communication and content consumption in recent months. Social distancing has severely limited outdoor activity for all age groups across the globe, leaving the online world as a primary mode of education, communication and entertainment. Use of streaming services, online gaming, social media, videoconferencing for personal, corporate, and education purposes is on the rise given the pandemic and is expected to grow in coming years.
IDC expects the changes brought about due to the pandemic will significantly alter our daily lives in many ways.
- First, organizations have adapted to employees working remotely and will continue to do so past the pandemic.
- Second, entertainment content (streaming content services for movies, television series and sports) and revenue generation from online advertising will continue to grow exponentially as content creators capitalize on an existing base of worldwide audience.
- Third, organizations will continue to leverage smart video for wide variety of use cases such as health monitoring in public areas, physical security, transportation, manufacturing, etc.
For consumers of this video and video-like content, quality of experience, low latency, flexibility of device and mobility are extremely important. For content creators and distributors, it is important for the underlying infrastructure ecosystem to function like a well-oiled machine that enables collaboration, time to market, monetization and secure delivery of content. This means that the infrastructure requirements deployed to support content workflow – from creation to delivery to archival – must adapt to the changing demands.
Data or Content?
Two terms that are often used in the context of unstructured data, particularly video and video like content are data and content. It is often difficult to differentiate the two terms and are used interchangeably but for the Content Infrastructure taxonomy, IDC is defining two important terms as follows:
- Data refers to various components of what makes video content ready for consumption. For example, raw or unedited videos captured using cameras, edited videos, supplemental footage included with final content, special visual and audio effects, etc. are considered individual components of the final video content and therefore referred to as data.
- Content is the combination of various data components mentioned above ready for consumption in finished form. Movies, television shows, streamed live events, online gaming is final content ready for delivery and consumption. The combination of various data components allows for consumers of the content to feel a sense of meaning, context and a beginning and end of the topic the video captures.
IDC’s Take on Content Infrastructure
The media & entertainment (M&E) industry is the turning the corner to becoming an industry that is at the forefront of technology. The following chart shows IDC’s take on the Content Infrastructure market beginning from content creators, post-production, distribution & delivery, consumption and content consumption via endpoints.
This taxonomy is limited to Content Infrastructure for entertainment related content. IDC plans to expand the Content Infrastructure research to include video and video-like data for corporate, education and government in the near future.
The Content Infrastructure market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years owing to increased professional and end-user content generation and growing online viewership. This complexity of market is intensified not only by the amount of content generated, audience and their location of consumption but also by the ecosystem of partners and providers that make content streaming a possibility.
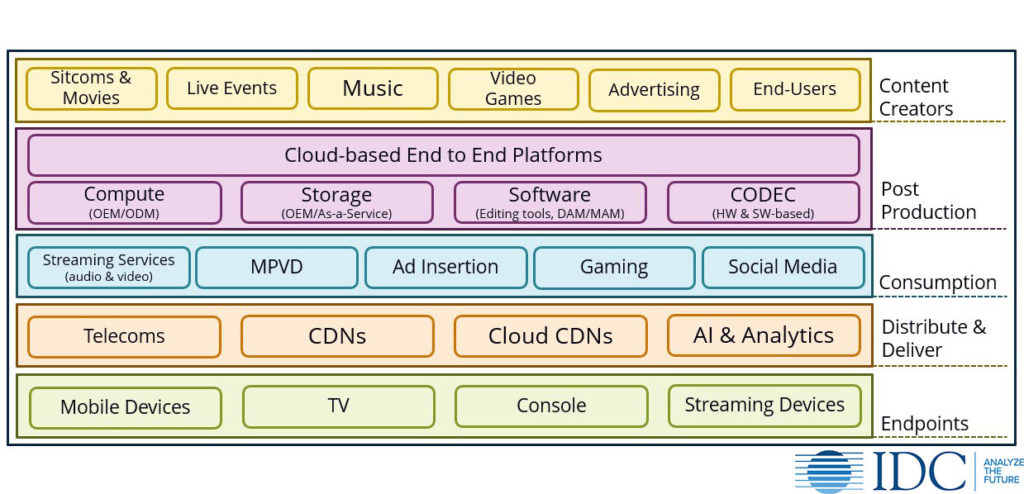
Speed and agility are key drivers to monetizing content and therefore the underlying infrastructure must lend itself to these goals. This industry has seen an increased adoption of accelerator technology, all-flash and all-NVMe storage systems, high-performance parallel file systems as well as object stores, cloud-based compute and storage resources, as well as integrations with state-of-the-art editing and asset management tools across all of the above categories in order to create and deliver high quality content in a timely fashion. Cloud-based end-to-end (from ingest to delivery and archive) media services are expected to grow due to ease of scaling as well as adjacent services such as artificial intelligence and analytics.
CDN’s will play an important role in this market ensuring global heterogenous content delivery with continued innovation around bandwidth, latency, resiliency, and global availability for best user experience. In an age of personalized content serving and hyper localization, ad-serving and live television must also follow the same concepts. Therefore, artificial intelligence and analytics will play a greater role in the Content Infrastructure market going forward.
At the core, IDC believes Content Infrastructure should support three key areas:
- enhanced user experience
- time to market
- secure means of content monetization
In the coming months IDC’s Content Infrastructure research will span infrastructure across all 5 categories as reflected in Figure 1.
Learn more about the Content Infrastructure taxonomy and the ecosystem of players in IDC’s IDC Market Glance: Content Infrastructure, 2Q20:




