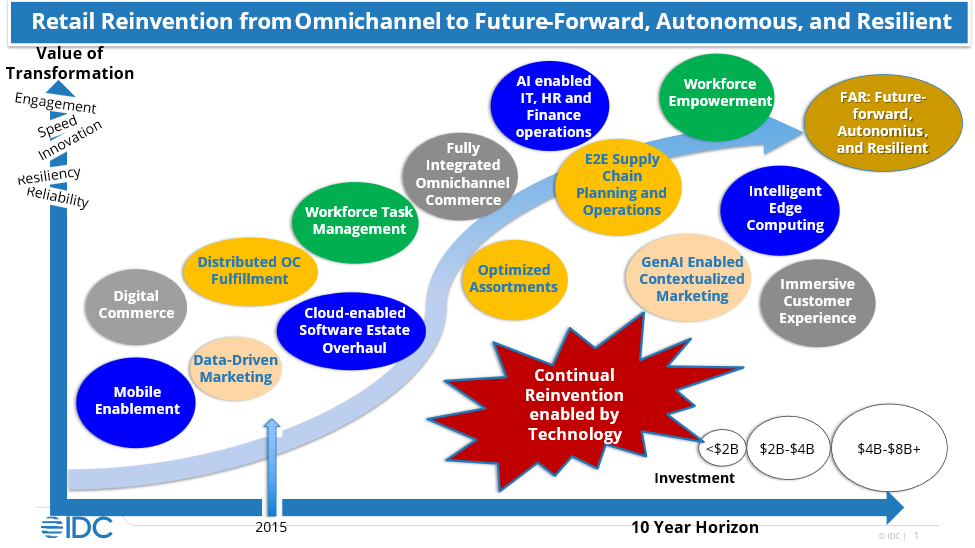
The retail industry has been on a transformative journey since the dawn of omnichannel in 2009, evolving through digital transformation, AI and mobile everywhere, to the current era of Generative AI and intelligent edge computing.
This evolution has not only reshaped retail software, hardware, and services investments but also significantly impacted the supply chain and frontline workforce. The industry is on a journey to becoming future-forward, autonomous, and resilient (FAR), leveraging AI and GenAI to take retail reinvention even farther. Let’s explore this comprehensive transformation and its implications for the future of retail. Retailers can continue to improve on omnichannel by focusing on the customer, with the most efficient product flows and engaging employee experiences in mind. The path from Omnichannel to FAR is continuous and ongoing as illustrated in the following graphic.
The birth of Omnichannel
I am often credited with coining the term “omnichannel”, which was discussed internally at IDC in late 2008 but published in publicly available editorials in 2009 (RIS News and Chain Store Age). Omnichannel encapsulates a vision for a shopping experience that transcends traditional channel boundaries. This concept emerged from the recognition that consumers were no longer shopping in silos but were instead leveraging multiple channels simultaneously to make informed purchasing decisions.
At its core, omnichannel retailing is about creating a cohesive customer experience across all available shopping channels, including in-store, online, mobile, and social media. This approach is designed to meet the customer where they are, providing flexibility and convenience at every touchpoint.
Technology serves as the backbone of this new retail reality, enabling consumers to navigate through different channels seamlessly. Retailers leveraging cloud, AI, and mobile technologies are better positioned to offer these integrated experiences, thereby not only meeting but exceeding customer expectations.
The implications of this shift are profound. Omnichannel shoppers tend to spend 15-30% more than those who shop via a single channel. Moreover, their loyalty extends beyond mere transactions, influencing others in their network and contributing to a positive brand perception. Retailers that recognize and adapt to this behavior stand to gain significantly in terms of customer loyalty and spending. Omnichannel shoppers are the majority with 77.4% reporting that they actively shop in stores and online (IDC Retail Insights Consumer Sentiment Survey, June 2024). Add shopping within social media apps to the mix and omnichannel influence is even greater.
The Dawn of Omnichannel: Laying the Foundation
In 2009, the retail industry began to embrace the omnichannel approach, aiming to provide a seamless shopping experience across online and offline channels. Initial investments focused on software solutions for integrating these channels, such as eCommerce platforms and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems. Hardware investments aimed at enhancing the in-store experience with upgraded Point of Sale (POS) systems and in-store Wi-Fi. The supply chain saw the beginning of digital tracking systems, while the frontline workforce had to adapt to new technologies, requiring training and adjustments in their roles.
Digital Transformation: Expanding Capabilities
As the decade progressed, the focus shifted towards digital transformation, necessitating a broader range of investments. Retailers poured resources into developing mobile apps and optimizing websites for mobile shopping, recognizing the growing trend of smartphone usage. Cloud computing services became essential, offering the scalability needed to handle increasing online traffic and data storage. Hardware investments expanded to include ruggedized- and consumer- mobile devices and tablets for sales assistants and interactive kiosks to enrich the in-store experience. The supply chain benefited from investments in digital planning and logistics platforms, improving efficiency and visibility. The frontline workforce faced the challenge of integrating digital tools into their daily operations, necessitating ongoing training, and unleashing a desire to be connected to information to improve customer service. The era also saw a rise in cybersecurity investments, protecting the vast amounts of consumer data being collected. Regulations started emerging that require that retailers give Consumers choice in what and when data is collected with the ability to request that the data is not shared and/or deleted.
AI and Mobile Everywhere: Enhancing Operations and Improving Profitability
The late 2010s marked the maturation of the “AI and Mobile Everywhere” era, and the 2020 pandemic accelerated investment in touch-free technologies and flexible last-mile and omnichannel order orchestration capabilities. Retailers started integrating AI across various operations, from personalized recommendations, product assortments, pricing, and promotions, to inventory management. Data management and governance was prioritized as retailers sought to centralize one version of the truth for customer data (in CDP’s), product data (in MDM’s and / or PIM’s), and inventory data (in a central repository (ERP, WMS, or Merch Planning) supporting merchandising, supply chain, and commerce applications). Hardware investments included AI-enabled cameras and sensors for inventory tracking and customer movement analysis within stores. Services expanded to include AI training for employees and partnerships with AI technology providers to develop custom solutions. This era emphasized the importance of data analytics, with significant investments in tools to analyze consumer behavior and preferences
The supply chain saw the introduction of AI for predictive analytics and autonomous vehicles and drones for delivery. Investments in AI-powered software solutions surged, alongside the adoption of integrated mobile technologies for enhanced customer engagement. The frontline workforce began to depend on AI and mobile tools for better customer service and workforce management self-service, improving experiences for the customer and workforce.
Generative AI and Intelligent Edge Computing
The exploration of Generative AI’s potential, coupled with advancements in intelligent edge computing, represents the latest phase in retail’s evolution. Software investments are increasingly directed towards Generative AI platforms capable of creating personalized content, designing new products, and enhancing customer service with sophisticated chatbots/virtual assistants. Hardware investments now focus on high-performance computing systems to support the demanding requirements of Generative AI algorithms. Distributed edge platforms, AI PC’s and AI-chips will improve compute response, throughput and efficiency, making AI at the edge very possible in stores. Services are evolving to include ethical AI consulting, ensuring that the use of Generative AI aligns with privacy and fairness standards. The supply chain is experiencing a revolution with AI-driven predictive analytics, autonomous systems, and real-time tracking. RFID mandates from a relatively short, but very important list of retailers will drive traceability and improved inventory control in non-food products. The frontline workforce will benefit as the focus on serving customers well is prioritized as routine tasks are automated.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that the retail industry’s technology investment landscape will continue to evolve. The integration of technology into retail operations has moved from a competitive advantage to a necessity. Retailers must stay abreast of technological advancements, such as Generative AI, to remain relevant in a rapidly changing market
Retailers will test, pilot and implement capabilities that improve business performance and protect the future of the business. Forever pragmatic, AI and Gen AI will be applied where the economics of investment make sense. Becoming future-forward, autonomous, and resilient requires a holistic approach that encompasses technological innovation, cultural transformation, and strategic partnerships. By embracing these principles, retailers can navigate the challenges of the digital era, meet evolving consumer expectations, and secure a competitive edge in the marketplace. The journey towards this transformation may be complex, but the rewards—sustained growth, operational efficiency, and enhanced customer loyalty—are well worth the effort.
Part 2 will continue with advice for the technology buyer as they seek to transform with FAR in mind.
Discover how IDC’s AI Use Case Discovery Tool can elevate your AI strategy—learn more here.




